 |
|
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 |
| Source file: | hex.{c, cpp, java} |
| Input file: | hex.in |
 |
|
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 |
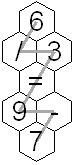
An amusing puzzle consists of a collection of hexagonal tiles packed together with each tile showing a digit or '=' or an arithmetic operation '+', '-', '*', or '/'. Consider continuous paths going through each tile exactly once, with each successive tile being an immediate neighbor of the previous tile. The object is to choose such a path so the sequence of characters on the tiles makes an acceptable equation, according to the restrictions listed below. A sequence is illustrated in each figure above. In Figure 1, if you follow the gray path from the top, the character sequence is"6/3=9-7". Similarly, in Figure 2, start from the bottom left 3 to get "3*21+10=73".
There are a lot of potential paths through a moderate sized hex tile pattern. A puzzle player may get frustrated and want to see the answer. Your task is to automate the solution.
The arrangement of hex tiles and choices of characters in each puzzle satisfy these rules:
To have an acceptable solution from the characters in some path, the expressions on each side of the equal sign must be in acceptable form and evaluate to the same numeric value. The following rules define acceptable form of the expressions on each side of the equal sign and the method of expression evaluation:
With the assumptions above, an acceptable expression will never involve an intermediate or final arithmetic result with magnitude over three million.
Input: The input will consist of one to fifteen data sets, followed by a line containing only 0.
The first line of a dataset contains blank separated integers r c, where r is the number of rows in the hex pattern and c is the number of entries in the odd numbered rows. The next r lines contain the characters on the hex tiles, one row per line. All hex tile characters for a row are blank separated. The lines for odd numbered rows also start with a blank, to better simulate the way the hexagons fit together. Properties 1-5 apply.
Output: There is one line of output for each data set. It is the unique acceptable equation according to rules 6-10 above. The line includes no spaces.
| Example input: | Example output: |
| 5 1 6 / 3 = 9 - 7 3 3 1 + 1 * 2 0 = 3 3 7 5 2 9 - * 2 = 3 4 + 8 3 4 / 0 |
6/3=9-7 3*21+10=73 8/4+3*9-2=43 |
Last modified on October 26, 2008 at 9:27 PM.